Embarking on the journey of seed saving is a rewarding endeavor for any edible gardener. Not only does it allow you to preserve the unique characteristics of your favorite vegetables, but it also promotes self - sufficiency and biodiversity in your garden. In this article, we will explore the best vegetables for seed saving and provide you with valuable tips on collecting and storing these precious seeds for next year's garden.
### Best Vegetables for Seed Saving
#### Tomatoes
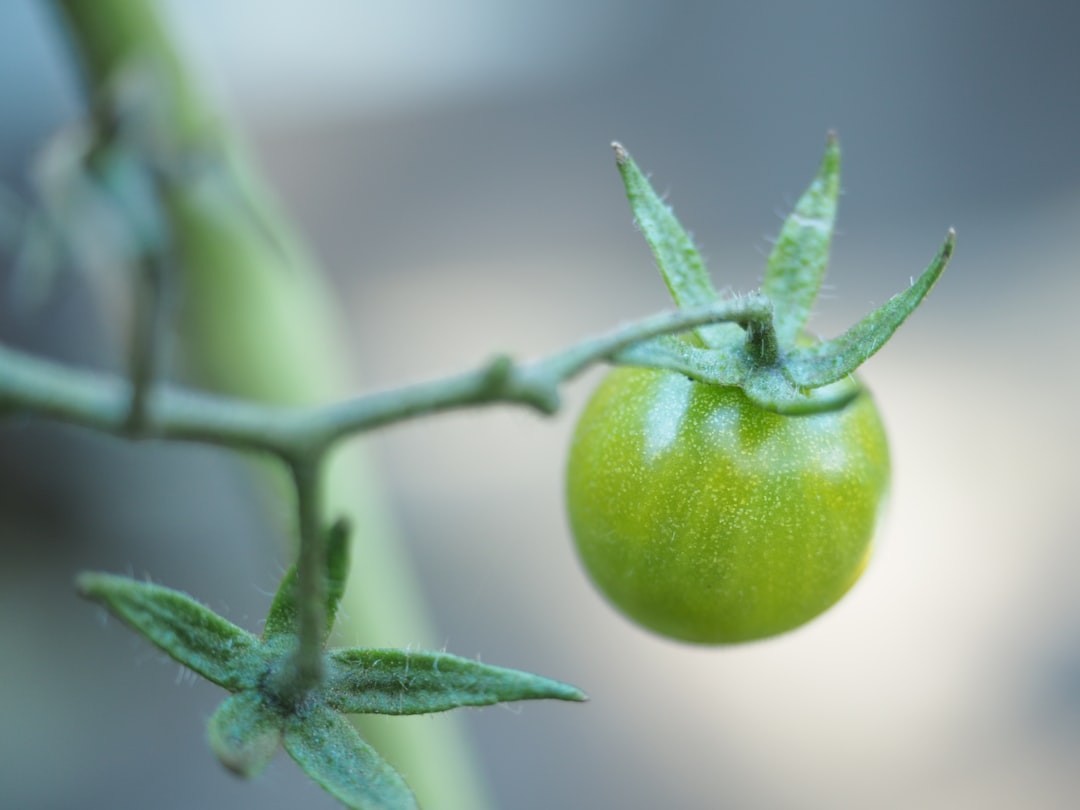
Tomatoes are a staple in many vegetable gardens, and they are relatively easy to save seeds from. Choose open - pollinated or heirloom varieties, as hybrid tomatoes may not produce true - to - type plants from saved seeds. To save tomato seeds, cut the tomato in half horizontally and squeeze the pulp and seeds into a container. Add a little water and let the mixture ferment for a few days. This fermentation process helps to remove the gelatinous coating around the seeds. After fermentation, rinse the seeds thoroughly and let them dry on a paper towel. Once dry, store the seeds in a cool, dry place.
#### Peppers
Peppers, both sweet and hot, are another great option for seed saving. Similar to tomatoes, select open - pollinated varieties. Cut the pepper open and remove the seeds. Spread the seeds out on a plate or a piece of paper to dry. Make sure they are completely dry before storing them. You can store pepper seeds in an envelope or a small glass jar.
#### Beans
Beans are excellent candidates for seed saving. They are self - pollinating, which means the seeds will produce plants that are very similar to the parent plant. Let the bean pods dry on the plant until they are brittle. Then, remove the pods and shell the beans. Store the dried beans in a sealed container. They can remain viable for several years if stored properly.
#### Lettuce
Lettuce is a fast - growing vegetable that can be easily saved for seeds. Allow some of your lettuce plants to bolt (go to seed). The flowers will turn into fluffy seed heads. Once the seed heads are dry, gently shake them over a container to collect the seeds. Lettuce seeds are very small, so be careful not to lose them. Store the seeds in a cool, dark place.
### Tips for Collecting and Storing Vegetable Seeds
#### Collecting Seeds
When collecting seeds, it is important to use clean tools to avoid cross - contamination. Make sure the plants you are collecting seeds from are healthy and free of diseases. Label your seed containers clearly with the name of the vegetable, the variety, and the date of collection. This will help you keep track of your seeds and ensure you know what you are planting next year.
#### Drying Seeds
Proper drying is crucial for seed storage. Spread the seeds out in a single layer on a clean surface. Avoid direct sunlight, as it can damage the seeds. A well - ventilated area is ideal for drying. Stir the seeds occasionally to ensure even drying. The seeds should be completely dry before storing them. You can test the dryness by trying to break a seed. If it snaps, it is dry enough.
#### Storing Seeds
Store your dried seeds in airtight containers. Glass jars, plastic bags, or envelopes can all be used. Place a desiccant, such as a silica gel packet, in the container to absorb any moisture. Keep the containers in a cool, dark, and dry place. A refrigerator or a cellar is a good option. Check your stored seeds periodically for signs of mold or moisture. If you notice any issues, remove the affected seeds and adjust the storage conditions.
### Conclusion
Seed saving is an essential skill for edible gardeners. By choosing the right vegetables and following proper collection and storage techniques, you can ensure a bountiful harvest in your garden year after year. So, start saving those seeds today and watch your garden thrive with the fruits of your labor.
New